Cold Chamber vs. Hot Chamber Die Casting : Choosing the Best Option for Your Project
Choosing between cold chamber and hot chamber die casting might seem daunting at first, but it’s actually an exciting opportunity to tailor the right solution for your unique project. By diving into the key differences—from metal types to production efficiencies—you’ll discover which method aligns perfectly with your goals. Die casting is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, celebrated for its precision, durability, and adaptability. Let’s explore these methods in detail.
1. Operating Principles
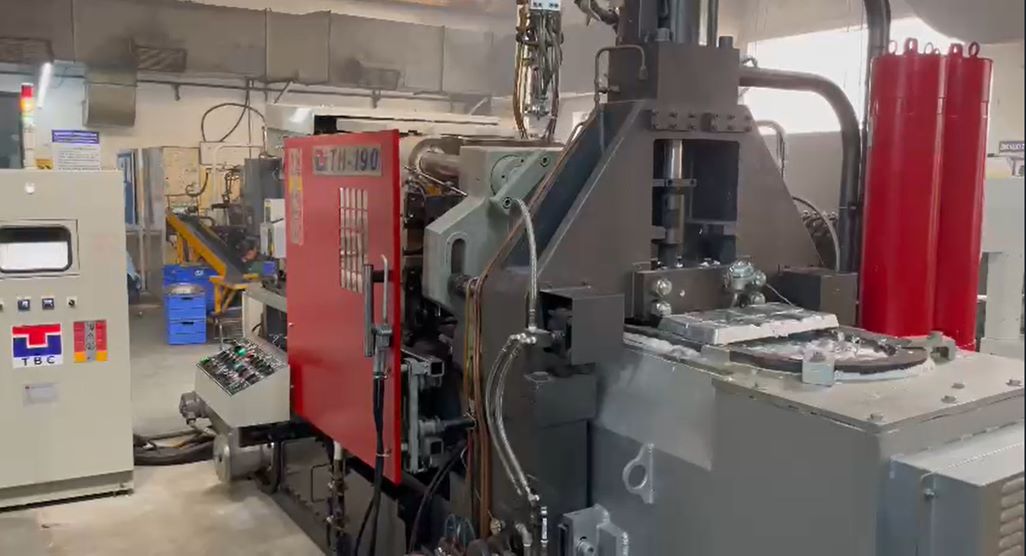
Cold Chamber Machines
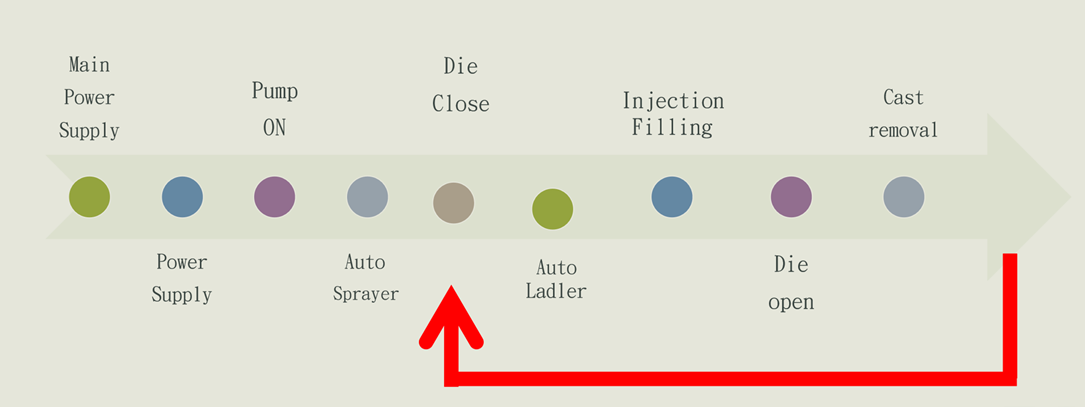
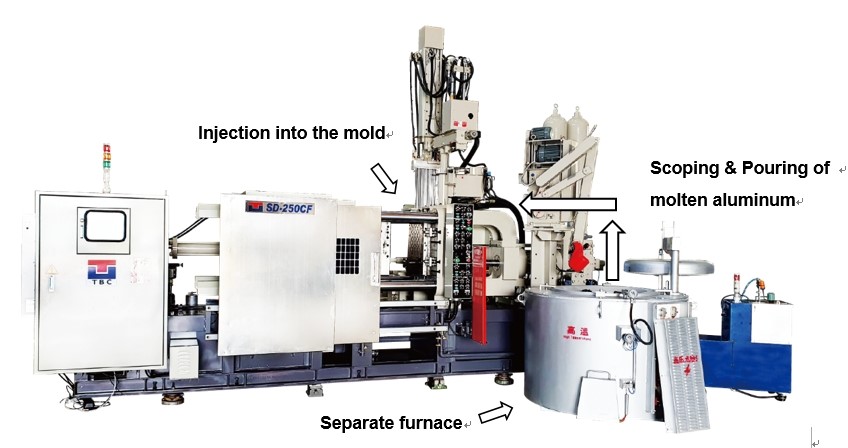
These machines are designed for metals requiring high temperatures to melt. The molten metal is poured into a separate cold chamber and then injected into the mold under high pressure. This method is perfect for materials like aluminum and copper alloys, which melt at around 660°C (1220°F) or higher. While highly precise, the process takes more time and effort due to its complexity, making it an essential part of the Aluminum Die Casting Process.

|
|
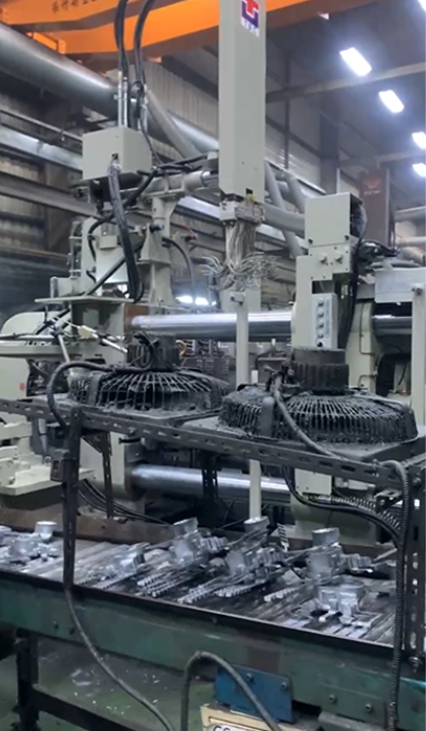
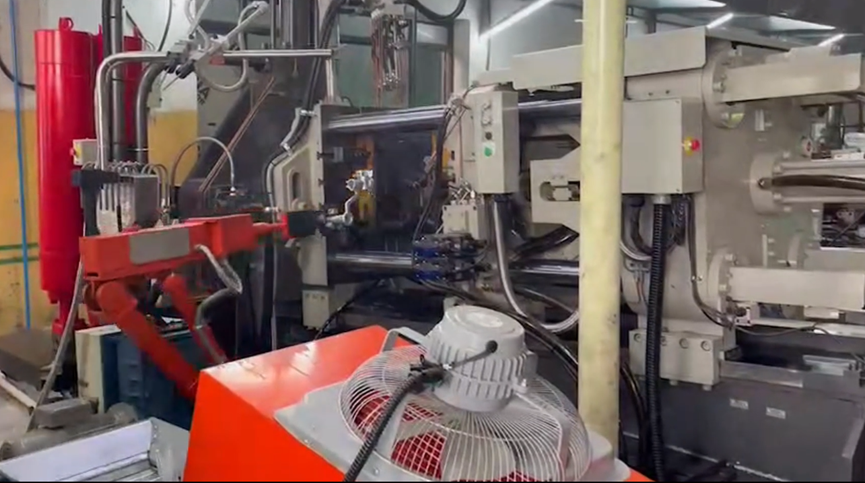
Hot Chamber Machines
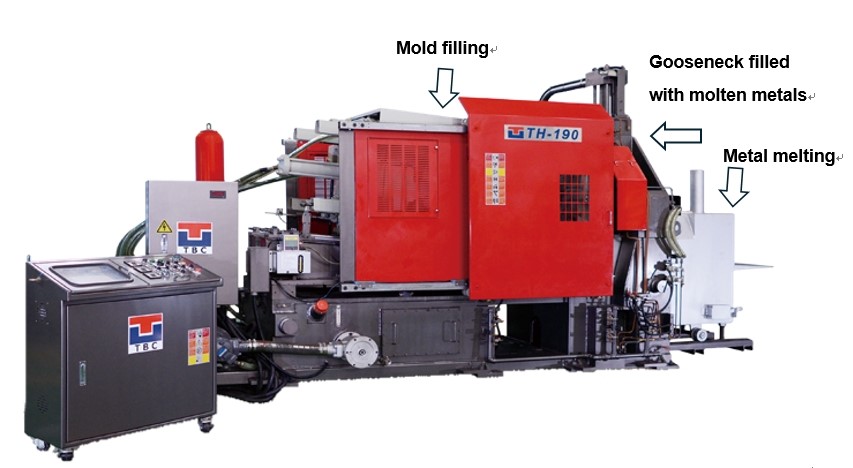
Hot chamber machines melt the metal directly in the injection system. This setup makes them faster and more efficient, particularly for low-melting-point metals like zinc and tin, which melt below 500°C (932°F). These machines are often part of Automated Die Casting systems, designed for high-volume production. However, they’re unsuitable for high-melting-point metals, as these could damage the equipment.


2. Structure & Injection System
Cold Chamber Machines
Cold chamber machines feature a larger structure and require a separate furnace to melt the metal, which is then transferred to the injection system. This design supports high-pressure handling for tough metals but increases maintenance complexity.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines are compact, with an integrated furnace and injection system. This streamlined design eliminates the need for molten metal transfer, enabling faster production cycles. However, the continuous exposure to molten metal makes regular maintenance to prevent corrosion essential.
3. Part Size and Complexity
Cold Chamber Machines
Cold chamber machines excel at producing larger or highly intricate parts. If your project involves complex designs requiring exceptional precision, this method is the ideal choice.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines are better suited for smaller, high-volume components. They deliver excellent results for detailed parts made from low-melting-point metals, offering a faster production process.
4. Maintenance and Durability
Cold Chamber Machines
With more moving parts and a complex structure, cold chamber machines demand frequent maintenance. Key areas include the hydraulic system and high-pressure components, which require regular inspection to ensure reliable performance.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines, with their simpler design, have lower maintenance needs overall. However, components like nozzles and pistons in constant contact with molten metal should be checked and replaced periodically to prevent corrosion.
5. Production Efficiency
Cold Chamber Machines
Cold chamber machines prioritize precision over speed, making them ideal for low-volume projects where quality matters most. The additional steps, such as transferring molten metal, add time but ensure superior results for intricate designs.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines are built for speed and volume. Their integrated system eliminates the need for metal transfer, resulting in faster cycles and cost-effective production for large-scale manufacturing.
6. Environmental Considerations
Cold Chamber Machines
Cold chamber machines are energy-intensive, primarily because they rely on separate furnaces and high-pressure systems to handle tough metals. However, their compatibility with recyclable materials like aluminum offsets some of their environmental impact.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines shine in energy efficiency, leveraging their integrated design and rapid cycles to minimize waste and maximize throughput. They are often the greener choice for high-volume production.
7. Cost Analysis
Cold Chamber Machines
These machines require a higher initial investment due to their larger structure and additional components, such as separate furnaces. Operating costs are also higher because of longer cycle times and greater energy usage. However, they’re a worthwhile investment for projects demanding high precision.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines are more cost-effective, both in terms of initial investment and operational expenses. Their compact design and faster production cycles reduce labor and energy costs, making them an economical choice for mass production.
8. Applications by Industry
Cold Chamber Machines
Cold chamber machines are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision and durability are critical. Common applications include engine components, structural parts, and high-performance materials.
Hot Chamber Machines
Hot chamber machines are favored in industries like consumer electronics and small appliance manufacturing. They’re ideal for producing small, intricate parts like connectors, housings, and fasteners at high volumes.
9. Comprehensive Comparison Table
| Feature | Cold Chamber Die Casting | Hot Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Type | High-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, copper) | Low-melting-point metals (e.g., zinc, tin, magnesium) |
| Melting Point | Around 660°C (1220°F) or above | Below 500°C (932°F) |
| Structure Size | Larger structure; requires separate furnace | Compact structure; furnace integrated with injection system |
| Injection System | Complex; handles high pressures | Simpler; suitable for lower pressures |
| Efficiency | Lower; longer cycle times | Higher; faster cycle times |
| Maintenance Needs | Higher; more components to maintain | Lower; focus on corrosion-prone areas |
| Durability | Robust; regular inspection needed | Durable; periodic replacement of high-temp parts |
| Part Size | Suitable for larger parts | Ideal for small components |
| Complexity | Handles intricate, precise designs | Best for detailed but smaller parts |
| Production Volume | Low-volume production | High-volume production |
| Preparation Time | Longer due to metal transfer | Shorter with integrated furnace and injection system |
| Ideal Use Case | High-precision, low-volume production | High-volume, cost-effective manufacturing |
Crafting the Perfect Cast : A Die Casting Finale
Die casting isn’t just a process; it’s the heart of countless industries, shaping everything from the smallest electronics to robust engine components. The decision between cold chamber and hot chamber die casting isn’t a mere technical choice but a strategy that defines your project’s success.
If your focus is on precision and strength, cold chamber die casting is your ally, perfect for larger, intricate designs and metals that stand the heat. Think automotive and aerospace marvels—cold chamber machines excel in crafting components where every detail matters.
On the flip side, if speed and efficiency drive your goals, hot chamber die casting is a game-changer. Its seamless, integrated design makes it the champion of high-volume, cost-effective production—a favorite for industries like consumer electronics and appliances.
Choosing the right path isn’t about compromise; it’s about optimization. By understanding these distinctions, you equip yourself to harness the best of what die casting offers, bringing your vision to life with precision and efficiency.
If you're looking for reliable and efficient die casting machines, TBC is here to help. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your manufacturing needs.


